|
 INVENTIONS THAT MADE OUR WORLD
INVENTIONS THAT MADE OUR WORLD
This page gives an impression of how our
civilization developed to its present state. It may help us understand our
modern infatuation with new technology in our profession careers, as well as our
personal affairs.
BCE = Before Current Era
Ma = Million years ka = 1000 years
 Paleolithic era
Paleolithic era
3.3 Ma: Sstone tools, Lake Turkana, Kenya
2.4 Ma: Oldowan - struck stone tools, in East Africa 
2.0 Ma: Earliest use of a language
1.65 Ma: Acheulean - struck and reworked stone tools, in Kenya
1.4 Ma: Knife in Ethiopia
1.0 Ma: Controlled fire and sterilization of food and water (cooking)
in East Africa
500 ka: Shelter construction
100-500 ka: Clothing
430 ka: Engraving on a shell, Indonesia
400 ka: Pigments in Zambia
400 ka: Spears in Germany
200 ka: Burial in Africa
140 ka: Bone tools in Africa
140 ka: Shellfishing in Africa
100 ka: Lithic blades in Africa and Near East
75 ka: Jewelry, Blomberg cave
60 ka: Ships probably used by settlers of New Guinea
50 ka: Bow
43 ka: Flute in Slovenia
43 ka: Mining in Swaziland and Hungary
40 ka: Cave paintings
40 ka: Shoes in China
37 ka: Tally sticks in Swaziland
30 ka: Sewing needles
28 ka: Twisted rope
26 ka: Ceramics in Moravia
25 ka: Atlatl in Northwest Africa
20 ka: Mud huts
15 ka: Boomerang in Australia
12 ka: Basket weaving
  Antiquity
Antiquity
 10th Millennium BCE
10th Millennium BCE
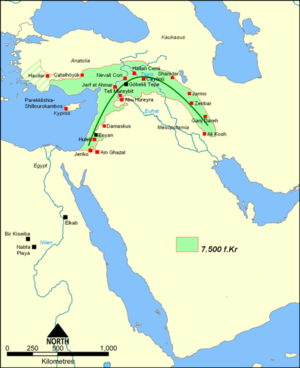
Agriculture in the Fertile Crescent (Neolithic Revolution)
Alcoholic beverages in the Fertile Crescent
Organized religion
Adobe in the Near East
9500 BCE: Granary in the Jordan Valley
 9th Millennium BCE
9th Millennium BCE
8700 BCE: Metalworking (copper pendant) in Mesopotamia (Iraq)
 8th Millennium BCE
8th Millennium BCE
Animal husbandry in the Near East 
Copper smelting in Serbia
 7th Millennium BCE
7th Millennium BCE
7000 BCE: Dental drill in Mehrgarh, Pakistan
Cloth woven from flax fiber
 6th Millennium BCE
6th Millennium BCE
6200 BCE: Map, in Çatalhöyük
Irrigation in the Fertile Crescent
Beer in Sumer, Mesopotamia (Iraq)
City in Mesopotamia (Iraq)
Plough in Mesopotamia (Iraq)
 5th Millennium BCE
5th Millennium BCE
Beer and bread in Egypt
Wheel and axle combination in Mesopotamia
Ice skate in Scandinavia
 4th Millennium BCE
4th Millennium BCE
4000 BCE: Canal in Mesopotamia
4000 BCE: Stone paved street Ur Iraq
3807-3806 BCE: Timber-engineered roadway in England
3630 BCE: Silk in China
3600 BCE: Free-standing Masonry Architecture at Ġgantija, Gozo,
Malta
3500 BCE: Plywood in Egypt
3500 BCE: Writing in Sumer
3500 BCE: Carts in Sumer
3100 BCE: Drainage in the Indus Valley India/Pakistan
3000 BCE: Sailing
3000s BCE: Rice in India
3000s BCE: Reservoir in the Indus Valley
Bronze in Susa Iran
Cement in Egypt
River boats in Egypt
Noodle in China
Comb in Persia (probably earlier)
  3rd Millennium BCE
3rd Millennium BCE
2800 BCE: Button in the Indus Valley
2800 BCE: Soap in Mesopotamia
2700 BCE: Plumbing in the Indus Valley
2630-2611 BCE: Step pyramid: Imhotep in Egypt 
2600s BCE: Papyrus: Imhotep in Egypt
2600s BCE: Suture: Imhotep in Egypt
2600s BCE: Pharmaceutical cream: Imhotep in Egypt
2600s BCE: Chariot in Mesopotamia
2500 BCE: Arch in Mohenjo-daro (Indus Valley
2400 BCE: Shipyard in Lothal (Indus Valley
2400 BCE: Dock in Lothal (Indus Valley
2000 BCE: Currency
Aqueduct in Egypt and Indus Valley
Dagger in Near East
Sickle-sword in Sumer
Alphabet in Phoenicia
Candles in Egypt
Ink in China
Sledges in Scandinavia
Ski in Scandinavia
 2nd Millennium BCE
2nd Millennium BCE
Iron in Anatolia, Caucasus and India
Perfume: Tapputi in Mesopotamia
Bronze Age sword in Mesopotamia
Glass in Egypt
Rubber in Mesoamerica
Spoked-wheel chariot Indo-Iranians
Water clock in Egypt
Iron Age sword Proto-Celtic
Bells in China
Fork in China
Umbrella in Mesopotamia
Calibration in the Indus Valley
Metrology in the Indus Valley
1300–1000 BCE: Zinc in India
1000 BCE: Coins in China
1000 BCE: Lens in Assyria
1000 BCE: Central heating: Ondol in Korea
1000 BCE: Underfloor heating: Ondol in Korea
 1st Millennium BCE
1st Millennium BCE
Cautery in Rome
Speculum in Rome
Cross-bladed scissors in Rome
Surgical needle in Rome
Cataract surgery in Rome
750 BCE: Celestial spheres in Greece
700 BCE: Button in Greece
700 BCE: Chain pump in Babylonia
600 BCE: Latin alphabet in Rome
600 BCE: Chopsticks in China
592 BCE: Anchor in Greece
500s BCE: Sugar in India
500s BCE: Dental bridge in Etruria
500s BCE: Kite: Lu Ban in China
500s BCE: Maps in Greece
500s BCE: Plastic surgery: Sushruta in India
500s BCE: Cosmetic surgery: Sushruta in India
500s BCE: Iron plough in China
499-477 BCE: Horse collar in China
475 BCE: Scythed Chariot: Ajatashatru in India
400s BCE: Linguistics: in India
400s BCE: Traction trebuchet in China
400s BCE: Catapult in Greece
400s BCE: Cast iron in China
400s BCE: Crossbow in China
 350 BCE: Water wheel in India 350 BCE: Water wheel in India
350 BCE: Watermill in India
300s BCE: Wootz steel in India
300s BCE: Aqueduct in Rome (This one is in Segovia, Spain) 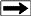
300s BCE: Compass in China
300s BCE: Star catalogues: Gan De and Shi Shen
300s BCE: Encyclopedia: Speusippus in Greece
300s BCE: Screw: Archytas
300s BCE: India ink in India
200s BCE: Diamond (gemstone) in India
200s BC: Clockwork escapement mechanism: Philo of Byzantium of
Greece
300-100 BCE: Blast furnace in China
300-100 BCE: Cupola furnace in China
300-100 BCE: Pig iron in China
285 BCE: Suspension bridge in China
250 BCE: Lever in Greece
210 BCE: Chromium use in China
200s BCE: Compound pulley: Archimedes
200s BCE: Odometer: Archimedes
200s BCE: Archimedes' screw: Archimedes
200s BCE: Cashmere wool in India
200s BCE: Contour canal: Shi Lu in China
200s BCE: Lock gate in China
200s BCE: Stupa in India
200s BCE: Pagoda in India
202-1 BCE: Bellows in China
200 BCE: Horseshoe in Rome
150s BCE: Clockwork (Antikythera mechanism)
150s BCE: Astrolabe: Hipparchus
100s BCE: Big-toe stirrup in India
100 BCE: Glassblowing in Rome
100s BCE: Parchment in Pergamon
100 BCE: Heavy plough in China
100s BCE: Wheelbarrow in China
100 BCE: Trip hammer in China
52 BCE: Armillary sphere: Geng Shouchang in China
40 BCE: Rolling-element bearing in Roman ship
21 BCE: Collapsible umbrella: Wang Mang
Catapult in Near East
South Pointing Chariot in China
Differential gear in China and Greek island of Antikythera
Flash lock in China
Bookbinding in India
Blowgun in India
Indigo dye in India
Iron pellet in India
Jute in Bengal
Neem toothbrush in India
 1st millennium
1st millennium
 1st-5th Centuries
1st-5th Centuries
1-100 CE: Junk ship in China
1-100 CE: Junk rudder in China
38 CE: Hydraulic-powered bellows: Du Shi
50 CE: Mouldboard plough in China and Gaul
77 CE: Encyclopedia: Pliny the Elder
 78-139: Hydraulic-powered armillary sphere: Zhang Heng 78-139: Hydraulic-powered armillary sphere: Zhang Heng
100s: Steam engine vending machine syringe force pump: Hero of
Alexandria in Roman Egypt
100s: Carding in India
105: Paper: Cai Lun in China
132: Rudimentary Seismometer: Zhang Heng in China 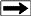
180: Rotary fan: Ding Huan in China
180: Winnowing fan: Ding Huan in China
200s: Kongming lantern (Hot air balloon) in China
200s: Horseshoes in Germany
200-400: Stepwell in India]
300s:
Combination lock in Roman Empire
300s: Toothpaste in Roman Egypt
400s: Horse collar in China
400s: Cotton gin in India
Fore-and-aft rig in India
Kamal in India
Prayer wheel: Tibet
Three-masted merchant vessel in China
Woodblock printing in China
 6th-8th Centuries
6th-8th Centuries
500s: Chess in India
500s: Ludo in India
589: Toilet paper: Yan Zhitui in China
605: Fully-stone open-spandrel segmental arch bridge: Li Chun in
China
618-700: Porcelain in China
618-907: Water-powered rotary fan in China
673: Greek fire flamethrower: Kallinikos of Heliopolis
700: Quill pen
700-900: Charitable trust in the Arab Empire
700s: Destructive distillation: Arabic chemists
700s: Inoculation: Madhav in India
721-815: Alembic: Geber (Jabir ibn Hayyan)
721-815: Still: Geber
721-815: Retort: Geber
721-815: Filtration: Geber
721-815: Crystallization: Geber
721-815: Pure distillation: Geber
721-815: Distilled alcohol: Geber
721-815: Distilled wine: Geber
721-815: Distilled beverage: Geber
721-815: Mineral acid: Geber
721-815: Nitric acid: Geber
721-815: Hydrochloric acid: Geber
721-815: Sulfuric acid: Geber
721-815: Uric acid: Geber
721-815: Acetic acid: Geber
721-815: Citric acid: Geber
721-815: Tartaric acid: Geber
721-815: Aqua regia: Geber
721-815: Cheese glue: Geber
721-815: Plated mail: Geber
721-815: Lustreware: Geber
721-815: Tin-glazing: Geber
721-815: Cucurbit: Geber
721-815: Evacuation tube: Geber
721-815: Aludel: Geber
721-815: Artificial pearl
721-815: Purified pearl
721-815: Dyed pearl
721-815: Dyed gemstone
721-815: Artificial gemstone
721-925: Rose water: Geber, Al-Kindi (Alkindus), Muhammad ibn
Zakarīya Rāzi (Rhazes)
721-925: Heated bath: Geber, Al-Kindi, Muhammad ibn Zakarīya
Rāzi
721-925: Sand bath: Geber, Al-Kindi, Muhammad ibn Zakarīya Rāzi
721-925: Funnel: Geber, Al-Kindi, Muhammad ibn Zakarīya Rāzi
721-925: Sieve: Geber, Al-Kindi, Muhammad ibn Zakarīya Rāzi
721-925: Filter: Geber, Al-Kindi, Muhammad ibn Zakarīya Rāzi
754: Pharmacy in Baghdad
754: Drugstore in Baghdad
758-764: Tar pavement in Baghdad
763-800: Public hospital: Harun al-Rashid
763-800: Psychiatric hospital in Baghdad
794: Paper mill in Baghdad
Amalgamation: Arabic chemists
Ceration: Arabic chemists
Dry distillation: Arabic chemists
Solution: Arabic chemists
Sublimation: Arabic chemists
Water purification: Arabic chemists
Purified water: Arabic chemists
Fusible alloy: Arabic chemists
Petrol: Arabic chemists
Apothecary: Arabic physicians
Lateen in India
 9th-10th Centuries
9th-10th Centuries
700-1000: Spinning wheel in India
800-850: Quadrant: Muhammad ibn Mūsā al-Khwārizmī (Algorismi)
800-850: Mural instrument: Muhammad ibn Mūsā al-Khwārizmī
800-850: Sine quadrant: Muhammad ibn Mūsā al-Khwārizmī
800-850: Horary quadrant: Muhammad ibn Mūsā al-Khwārizmī
800-850: Alhidade: Muhammad ibn Mūsā al-Khwārizmī
800-857: Under-arm deodorant: Ziryab
800-857: Beauty parlour: Ziryab
800-857: Bangs: Ziryab
800-857: Chemical depilatory: Ziryab
800-873: Valve: Banū Mūsā in Iraq
800-873: Float valve: Banū Mūsā
800-873: Feedback controller: Banū Mūsā
800-873: Float chamber: Banū Mūsā
800-873: Automatic control: Banū Mūsā
800-873: Automatic flute player: Banū Mūsā
800-873: Programmable machine: Banū Mūsā
800-873: Trick drinking vessels: Banū Mūsā
800-873: Gas mask: Banū Mūsā
800-873: Grab: Banū Mūsā
800-873: Clamshell grab: Banū Mūsā
800-873: Fail-safe system: Banū Mūsā
800-873: Mechanical musical instrument: Banū Mūsā
800-873: Hydro-powered organ: Banū Mūsā
800-873: Hurricane lamp: Banū Mūsā
800-873: Self-feeding oil lamp: Banū Mūsā
800-873: Self-trimming oil lamp: Ahmad ibn Mūsā ibn Shākir
800-1000: Wind powered gristmills in Afghanistan, Pakistan and Iran
800-1000: Sugar refinery in Afghanistan, Pakistan and Iran
800-1000: Metal block printing in Egypt
800-1000: Switch: Arabic engineers
800s: Stonepaste ceramics in Iraq
800s: Black powder in China
800s: Gunpowder in China
800s: Water turbine in the Arab Empire
800s: Universal sundial in Baghdad
 800s: Universal horary dial in Baghdad 800s: Universal horary dial in Baghdad
800s: Vertical-axle windmill in Afghanistan
800s: Naphtha in Azerbaijan
800s: Oil well in Azerbaijan 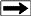
801-873: Pure alcohol: Al-Kindi (Alkindus)
801-1000: Municipal solid waste handling: Al-Kindi, Qusta ibn Luqa,
Muhammad ibn Zakarīya Rāzi, Ibn Al-Jazzar, al-Masihi
810-887: Glass from stones: Abbas Ibn Firnas in al-Andalus
810-887: convex lens
810-887: Clear colourless high-purity glass: Abbas Ibn Firnas
810-887: Metronome: Abbas Ibn Firnas
810-887: Artificial weather simulation: Abbas Ibn Firnas
813-833: Medical school: Al-Ma'mun
827: Mechanical singing bird automaton: Al-Ma'mun
836-1000: Erectile dysfunction treatment: Muhammad ibn Zakarīya
Rāzi, Thabit bin Qurra (Thebit), Ibn Al-Jazzar
853-929: Observation tube: Muhammad ibn Jābir al-Harrānī al-Battānī
(Albatenius)
852: Parachute: Abbas Ibn Firnas in al-Andalus
859: University: Princess Fatima al-Fihri
875: Hang glider: Abbas Ibn Firnas
875: Artificial wing: Abbas Ibn Firnas
875: Flight control frame: Abbas Ibn Firnas
865-900: Kerosene: Muhammad ibn Zakarīya Rāzi (Rhazes)
in Iraq
865-925: Hard soap: Muhammad ibn Zakarīya Rāzi
865-925: Chemotherapy: Muhammad ibn Zakarīya Rāzi
865-925: Antiseptic: Muhammad ibn Zakarīya Rāzi
900s: Banknote in China
900s: Fire lance in China
900s: Gun in China
900s: Milling factory in Baghdad
900s: Cartographic grid in Baghdad
900s: Graph paper in the Arab Empire
900s: Horizontal-axle windmill in Afghanistan, Pakistan and Iran
903-986: Timekeeping astrolabe: Abd al-Rahman al-Sufi (Azophi)
904: Fire Arrow in China
919: Double-piston flamethrower in China
984: Pound lock: Qiao Weiyo
953: Fountain pen: Al-Muizz Lideenillah of Egypt
960-1000: Restaurant in the Arab Empire
994: Astronomical sextant: Abu-Mahmud al-Khujandi in Persia
996: Geared mechanical astrolabe: Abū Rayhān al-Bīrūnī
Almucantar quadrant: Arabic astronomers
Navigational astrolabe: Arabic astronomers
Vertical sundial: Arabic astronomers
Polar sundial: Arabic astronomers
Coffee: Khalid in Ethiopia
Shaving soap: Arabic chemists
Plumb line: Arabic engineers
Reed level: Arabic engineers
Triangulation: Arabic engineers
Geared gristmill: Arabic engineers
Shatranj in Persia
Paned window in the Arab Empire
Street lamp in the Arab Empire
Sherbet in the Arab Empire
Soft drink in the Arab Empire
Syrup in the Arab Empire
Mercury escapement mechanism in the Middle East
Bridge dam in Iran
Milling dam in Iran
Diversion dam in Iraq
Public library in the Arab Empire
Lending library in the Arab Empire
Library catalog in the Arab Empire
Firecracker in China
Snakes and ladders in India
 2nd millennium
2nd millennium
 11th Century
11th Century
c. 1000: Pendulum: Ibn Yunus in Egypt
c. 1000: Injection syringe: Ammar ibn Ali al-Mawsili of Iraq
c. 1000: Hypodermic needle: Ammar ibn Ali al-Mawsili
c. 1000: Cataract extraction: Ammar ibn Ali al-Mawsili
c. 1000: Suction: Ammar ibn Ali al-Mawsili
1000: Ligature: Abu al-Qasim al-Zahrawi (Abulcasis) in Al-Andalus
1000: Adhesive plaster: Abu al-Qasim
1000: Curette: Abu al-Qasim
1000: Retractor: Abu al-Qasim
1000: Lithotomy scalpel: Abu al-Qasim
1000: Surgical catgut: Abu al-Qasim
1000: Surgical hook: Abu al-Qasim
1000: Surgical rod: Abu al-Qasim
1000: Surgical spoon: Abu al-Qasim
1000: Inhalational anaesthetic: Abu al-Qasim
1000: Anaesthetic sponge: Abu al-Qasim
1000: Oral anaesthesia: Abu al-Qasim
1000: Cotton dressing: Abu al-Qasim
c. 1000-1009: Monumental astrolabe: Ibn Yunus
c. 1000-1020: Heliocentric astrolabe: Al-Sijzi[
c. 1000-1037: Thermometer: Avicenna (Ibn Sina) in Persia
c. 1000-1037: Essential oil: Avicenna
c. 1000-1048: Orthographical astrolabe: Abū Rayhān al-Bīrūnī
in Persia
c. 1000-1048: Planisphere: Abū Rayhān al-Bīrūnī
c. 1000-1048: Star chart: Abū Rayhān al-Bīrūnī
c. 1000-1048: Laboratory flask: Abū Rayhān al-Bīrūnī
c. 1000-1048: Pycnometer: Abū Rayhān al-Bīrūnī
c. 1000-1048: Conical measure: Abū Rayhān al-Bīrūnī
c. 1000-1048: Geared mechanical lunisolar calendar analog computer:
Abū Rayhān al-Bīrūnī
c. 1000-1048: Fixed-wired knowledge processing machine: Abū Rayhān
al-Bīrūnī
1020: Mechanical astrolabe: Ibn Samh in Al-Andalus
1021: Magnifying glass: Ibn al-Haytham
1021: Curved mirror: Ibn al-Haytham
1021: Pinhole camera: Ibn al-Haytham
1021: Camera obscura: Ibn al-Haytham
1025: Cancer therapy: Avicenna
1025: Hirudotherapy: Avicenna
1025: Medicinal leech: Avicenna
1025: Calcium channel blocker: Avicenna
1025: Pharmacopoeia: Avicenna
1028-1087: Equatorium: Abū Ishāq Ibrāhīm al-Zarqālī (Arzachel)
in Al-Andalus
1028-1087: Universal astrolabe: Abū Ishāq Ibrāhīm al-Zarqālī
1031-1095: Raised-relief map: Shen Kuo
1038-1075: Flywheel: Ibn Bassal in Al-Andalus
1041: Movable type printing press: Bi Sheng in China
1044: Hand grenade: Zhen Tian Lei in China
1087: Almanac: Abū Ishāq Ibrāhīm al-Zarqālī
1088: Mechanical clock: Su Song
1088: Clock tower: Su Song
1088: Magnetic compass: Shen Kuo in China
1090: Belt drive: Qin Guan in in China
1090: Chain drive in China
1092: Astronomical clock: Su Song
1094: Printed star chart: Su Song
Coke fuel in China
Complex gearing: Ibn Khalaf al-Muradi in Al-Andalu
Epicyclic gearing: Ibn Khalaf al-Muradi in Al-Andalus
Segmental gearing: Ibn Khalaf al-Muradi in Al-Andalus
Geared mechanical clock: Ibn Khalaf al-Muradi in Al-Andalus
Weight-driven mechanical clock: Arabic engineers
Celestial globe: Arabic astronomers
Clear glass mirror in Al-Andalus
Cobwork in the Maghreb and Al-Andalus
 12th Century
12th Century
c. 1100: Framed bead abacus in China
1100-1150: Torquetum: Jabir ibn Aflah (Geber)
1100-1161: Tracheotomy: Ibn Zuhr (Avenzoar) in Al-Andalus
1119: Watertight hull compartment: Zhu Yu in China
1121: Steelyard: Al-Khazini in Persia
1121: Hydrostatic balance: Al-Khazini
1126: Fire arrow: Li Gang in China
1126: Rocket: Li Gang in China
1128: Cannon in China
1135-1200: Linear astrolabe: Sharaf al-Dīn al-Tūsī in
Persia
1150: Homing pigeons in Iraq and Syria
1154: Striking clock: Al-Kaysarani in Syria
1187: Counterweight trebuchet: Mardi bin Ali al-Tarsusi
1187: Mangonel: Mardi bin Ali al-Tarsusi
1190: Mariner's compass in Italy
Astrolabic quadrant in Egypt
Ventilator in Egypt
Bridge mill in Al-Andalus
Hydropowered forge in Al-Andalus
Finery forge in Al-Andalus
Central heating through underfloor pipes in Syria
Fireworks in China
Sunglasses in China
 13th Century
13th Century
c. 1200: Glass mirror in Europe
1206: Bolted joint lock
1206: Clock automaton: Al-Jazari
1206: Flow control regulator: Al-Jazari
1206: Closed-loop system: Al-Jazari
1206: Elephant clock: Al-Jazari
1206: Hand washing device: Al-Jazari
1206: Kitchen appliance: Al-Jazari
1206: Camshaft: Al-Jazari
1206: Segmental gear: Al-Jazari
1206: Suction pipe: Al-Jazari
1206: Suction piston pump: Al-Jazari
1206: Reciprocating piston motion: Al-Jazari
1206: Double-acting engine: Al-Jazari
1206: Humanoid robot: Al-Jazari
1206: Programmable robot: Al-Jazari
1206: Programmable analog computer: Al-Jazari
1206: Automatic gate: Al-Jazari
1206: Pointer: Al-Jazari
1206: Hydro-powered water supply system: Al-Jazari
1206: Geared water supply system: Al-Jazari[
1206: Laminate: Al-Jazari
1206: Mechanical template: Al-Jazari
1206: Paper model: Al-Jazar
1206: Calibration: Al-Jazari
1206: Sand casting: Al-Jazari
1206: Emery powder: Al-Jazari
1206: Crankshaft-driven chain pump: Al-Jazari
1206: Hydro-powered saqiya chain pump: Al-Jazari
1206: Intermittent working: Al-Jazari
1206: Hour hand: Al-Jazari
1232: Rocket launcher in China
1235: Geared astrolabe with analog computer calendar: Abi Bakr of
Isfahan
1259: Research institute: Nasīr al-Dīn al-Tūsī
1259: Observatory institution: Nasīr al-Dīn al-Tūsī
1260: Hand cannon in Egypt
1260: Explosive gunpowder in Egypt
1260: Explosive cannon in Egypt
1260: Handgun in Egypt
1260: Portable firearm in Egypt
1260: Cartridge in Egypt
1260: Dissolve talc in Egypt
1260: Fire protection in Egypt
1260: Fireproof clothing in Egypt
1270: Pure saltpetre: Hasan al-Rammah of Syria
1274: Siege cannon: Abu Yaqub Yusuf
1275: Torpedo: Hasan al-Rammah of Syria
1275: Restaurant menu in China
1277: Land mine: Lou Qianxia in China
c. 1296: Astronomical compass: Yemeni sultan al-Ashraf
1297-1298: Wooden movable type printing: Wang Zhen of China
Crankshaft-driven screw: Arabic engineers
Crankshaft-driven screwpump: Arabic engineers
Sandpaper in China
Solid-fuel rocket in China
Condom in Italy
Buttonhole in Germany
 14th Century
14th Century
1304-1375: Astrolabic clock: Ibn al-Shatir
1304-1375: Compendium instrument: Ibn al-Shatir
1304-1375: Compass dial: Ibn al-Shatir
1350: Rope bridge in Peru
1355: Bombard: Jiao Yu and Liu Ji
1355: Booster: Jiao Yu and Liu Ji
1355: Matchlock: Jiao Yu and Liu Ji
1355: Multistage rocket: Jiao Yu and Liu Ji
1355: Naval mine: Jiao Yu and Liu Ji
1355: Round shot: Jiao Yu and Liu Ji
1355: Shell: Jiao Yu and Liu Ji
1355: Wheellock: Jiao Yu and Liu Ji
1371: Polar-axis sundial: Ibn al-Shatir
32-point compass rose in the Arab world
Musket in China
Spherical astrolabe in the Middle East
 15th century
15th century
1400-1429: Plate of conjunctions: Jamshīd al-Kāshī
1400-1429: Planetary analog computer: Jamshīd al-Kāshī
1405-1433: Troopship: Zheng He
1405-1433: Treasure ship: Zheng He
1441: Rain gauge: Jang Yeong-sil
1450s: Alphabetic movable type printing press: Johannes Gutenberg
1451: Concave lens for eyeglasses: Nicholas of Cusa
1490-1492: Terrestrial globe: Martin Behaim
1494: Double-entry bookkeeping system: Luca Pacioli
1498: Bristle toothbrush: Hongzhi Emperor
Iron-chain suspension bridge in China
Arquebus in Europe
Rifle in Europe
 16th Century
16th Century
c. 1500: Ball bearing: Leonardo Da Vinci
c. 1500: Scissors: Leonardo Da Vinci
1524: Pocket watch: Peter Henlein
1540: Ether: Valerius Cordus
1551: Steam turbine: Taqi al-Din in Ottoman Egypt
1556: Spring-powered clock: Peter Henlein and Taqi al-Din
1559: Six-cylinder pump: Taqi al-Din
1565: Pencil: Conrad Gesner
1577-1580: Mechanical seconds clock: Taqi al-Din
1579: Prefabricated home: Akbar the Great
1579: Movable structure: Akbar the Great
1582: Autocannon: Fathullah Shirazi
1582: Multi-barrel gun: Fathullah Shirazi
1582: Grain-grinding carriage: Fathullah Shirazi
1589: Stocking frame: William Lee
1589-1590: Seamless celestial globe: Ali Kashmiri ibn Luqman
1589-1590: Seamless metal sphere: Ali Kashmiri ibn Luqman
c. 1590: Compound microscope: Zacharias Janssen, Hans Janssen, Hans
Lippershey
1592: Ironclad Warship: Yi Sun-sin
1593: Thermoscope: Galileo Galilei
Musket in Europe
Pencil in England
High-rise apartment buildings in Shibam
Tower blocks in Shibam
Vertical construction urban planning in Shibam
1596: Water closet=toilet Template: John Harrington&Thomas Crapper
 17th Century
17th Century
1609: Telescope: Hans Lippershey, Zacharias Janssen, Jacob Metius
1610: Flintlock: Marin le Bourgeoys
1620: Slide rule: William Oughtred
1623: Automatic calculator: Wilhelm Schickard
1631: Vernier scale: Pierre Vernier
1642: Adding machine: Blaise Pascal
1643: Barometer: Evangelista Torricelli
1645: Vacuum pump: Otto von Guericke
1657: Pendulum clock: Christiaan Huygens
1672: Steam car: Ferdinand Verbiest
1679: Pressure cooker: Denis Papin
1690: Polhem wheel: Christopher Polhem
1698: Steam engine powered water pump: Thomas Savery
1700: Piano: Bartolomeo Cristofori
 18th Century
18th Century
1701: Seed drill: Jethro Tull
1709: Iron smelting using coke: Abraham Darby
1711: Tuning fork: John Shore
1712: Steam piston engine: Thomas Newcomen
1714: Mercury thermometer: Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit
1731: Octant: John Hadley, Thomas Godfrey
1733: Flying shuttle: John Kay
1737: Marine chronometer (H1): John Harrison
1742: Franklin stove: Benjamin Franklin
1750: Flatboat: Jacob Yoder
1752: Lightning rod: Benjamin Franklin
1759: Shampoo: Sake Dean Mahomet of Bengal
1764: Spinning jenny: James Hargreaves/Thomas Highs
1767: Carbonated water: Joseph Priestley
1769: Water frame: Richard Arkwright/Thomas Highs
1769: Steam road vehicle: Nicolas-Joseph Cugnot
1775: Submarine Turtle: David Bushnell
1776: Steamboat: Claude de Jouffroy
1776: Watt steam engine: James Watt
1777: Card teeth making machine: Oliver Evans
1777: Circular saw: Samuel Miller
1779: Spinning mule: Samuel Crompton
1780s: Iron-cased rocket: Tipu Sultan in India
1780s: Metal-cylinder rocket artillery: Hyder Ali and Tipu Sultan in
India
1780s: Iron rocket artillery: Tipu Sultan of India
1783: Hot air balloon: Montgolfier brothers
1784: Bifocals: Benjamin Franklin
1784: Oil lamp: Aimé Argand
1784: Shrapnel shell: Henry Shrapnel
1785: Power loom: Edmund Cartwright
1785: Automatic flour mill: Oliver Evans
1786: Threshing machine: Andrew Meikle
1791: Artificial teeth: Nicholas Dubois De Chemant
1795: Appertization: Nicolas Appert
1798: Vaccination: Edward Jenner
1798: Lithography: Alois Senefelder
 19th Century
19th Century
1801: Jacquard loom: Joseph Marie Jacquard
1802: Screw propeller steamboat Phoenix: John Stevens
1802: Gas stove: James Sharp
1804: Road Locomotive: Richard Trevithick
1805: Submarine Nautilus: Robert Fulton
1807: Steamboat Clermont: Robert Fulton
1808: Band saw: William Newberry
1809: Arc lamp: Humphry Davy
1814: Steam locomotive (Blücher) George Stevenson,
Stockton &
Darlington Railway.
1815
First North American railroad charter for Camden & Amboy, not built.
1816: Miner's safety lamp: Humphry Davy
1816: Stirling engine: Robert Stirling
1816: Stethoscope: Rene Theophile Hyacinthe Laennec
1817: Draisine or velocipede (two-wheeled bicycle): Karl Drais
1817: Kaleidoscope: David Brewster
1818: Bicycle: Karl Drais
1821: Electric motor: Michael Faraday
1823: Electromagnet: William Sturgeon
1823: Lighter: Johann Wolfgang Döbereiner
1824: Portland cement: William Aspdin
1826: Photography: Joseph Nicéphore Niépce
1826: Internal combustion engine: Samuel Morey
1827
First railroad, Baltimore & Ohio Railroad, chartered in the United
States.
1827: Friction match: John Walker
1829
Delaware & Hudson Canal Co runs first steam-powered locomotive "Stourbridge
Lion" near Carbondale, Pennsylvania.
1830 Peter Cooper operates "Tom Thumb" - the first locomotive
manufactured in the United Stares - on the Baltimore & Ohio
Railroad.
1830: Thermostat: Andrew Ure
1830: Stenotype on punched paper strip: Karl Drais
1831: Multiple coil magnet: Joseph Henry
1831: Magnetic acoustic telegraph: Joseph Henry (patented 1837)
1831: Reaper: Cyrus McCormick
1831: Electrical generator: Michael Faraday, Ányos Jedlik
1834: The Hansom cab is patented
1834: Louis Braille perfects his Braille system
1834: Refrigerator: Jacob Perkins
1834: Combine harvester: Hiram Moore
1834: Electric Motor: Thomas Davenport
1835 Samuel Morse uses earlier technology (Joseph Henry, 1830) to
create telegraph.
1835: Revolver: Samuel Colt
1835: Electromechanical Relay: Joseph Henry
1835: Incandescent light bulb: James Bowman Lindsay
 1836
First steam locomotive "Dorchester" in Canada, Champlain & St
Lawrence RR. 1836
First steam locomotive "Dorchester" in Canada, Champlain & St
Lawrence RR.
1836: Sewing machine: Josef Madersberger
1837: US electric printing press patented by Thomas Davenport
(February 25)
1837: Steel plow: John Deere
1837: Standard diving dress: Augustus Siebe
1837: Camera Zoom Lens: Jozef Maximilián Petzval
1837: Magnetic telegraph: Samuel Morse
1838: Electric telegraph: Charles Wheatstone (also Samuel Morse)
1838: Closed diving suit with a helmet: Augustus Siebe
1839: Vulcanization of rubber: Charles Goodyear
1840: Artificial fertilizer: Justus von Liebig
1841: Saxophone:Adolphe Sax
1842: Superphosphate fertilizer: John Bennett Lawes
1842: Steam hammer: James Nasmyth
1842: Anaesthesia: Crawford Long
1843: Typewriter: Charles Thurber
1843: Fax machine: Alexander Bain
1843: Ice cream maker: Nancy Johnson
1843: Pile driver: James Nasmyth
1844: The safety match: Gustaf Erik Pasch
1844: Pulp wood for papermaking: Charles Fenerty (Nova Scotia,
Canada), and F.G. Keller (Germany)
1844:
First message transmitted over telegraph line completed between
Baltimore and Washington,
1845: Pneumatic tyre: Robert Thomson (inventor)
1846: First drilled oil well, Baku
 1846:
Distillation of kerosene from crude oil, Abraham Gesner (Canada) 1846:
Distillation of kerosene from crude oil, Abraham Gesner (Canada)
1846: Sewing machine: Elias Howe
1846: Rotary printing press: Richard M. Hoe
1849: Safety pin: Walter Hunt
1849: Francis turbine: James B. Francis
1849: Telephone: Antonio Meucci
1852: Airship: Henri Giffard
1852: Passenger elevator: Elisha Otis
1852: Gyroscope: Léon Foucault
1855: Bunsen burner: Peter Desaga
1855: Bessemer process: Henry Bessemer
1856: Celluloid: Alexander Parkes
1858: Undersea telegraph cable: Charles Wheatstone
1858: Mason jar: John L. Mason
1859: Lead acid battery: Gaston Plante
1860: Light Bulb, Sir Joseph Swan
1860: Linoleum: Fredrick Walton
1860: Repeating rifle: Oliver F. Winchester, Christopher Spencer
1860: Self-propelled torpedo: Giovanni Luppis
1861
Overland Telegraph and Pacific Telegraph complete transcontinental
system and quickly merge into Western Union.
1861: Ironclad (Battleship) USS Monitor: John Ericsson
1861: Siemens regenerative furnace: Carl Wilhelm Siemens
1862: Revolving machine gun: Richard J. Gatling
1862: Mechanical submarine: Narcís Monturiol i Estarriol
1862: Pasteurization: Louis Pasteur, Claude Bernard
1863: Player piano: Henri Fourneaux
1865: Roller Coaster: LaMarcus Adna Thompson
1865: Barbed wire: Louis Jannin
1866: Dynamite: Alfred Nobel
1868: Practical typewriter: Christopher Sholes, Carlos Glidden and
Samuel W. Soule, with assistance from James Densmore
1868: Oleomargarine: Mege Mouries
1869:
George Westinghouse patents automatic air brake.
1869: Vacuum cleaner: I.W. McGaffers
1870: Chewing gum: Thomas Adams
1870: Magic Lantern projector: Henry R. Heyl
1870: Stock ticker: Thomas Alva Edison
1871:
Andrew Smith Hallidie patents first cable car.
1871: First steam-powered elevated railway operation in New York
City.
1871: Cable car (railway): Andrew S. Hallidie
1873: Jeans: Levi Strauss
1873: Railway knuckle coupler: Eli H. Janney
1873: Modern direct current electric motor: Zénobe Gramme
1874: Barbed wire: Joseph Glidden
1874: Electric street car: Stephen Dudle Field
1874: DDT: Othmar Zeidler
1875: Dynamo: William A. Anthony
1875: Magazine (firearm): Benjamin B. Hotchkiss
1876: Carpet sweeper: Melville Bissell
1876: Gasoline carburettor: Daimler
1876: Loudspeaker: Alexander Graham Bell
 1876: Telephone patented, Alexander Graham Bell 1876: Telephone patented, Alexander Graham Bell
1877: Stapler: Henry R. Heyl
1877: Induction motor: Nikola Tesla
1877: Phonograph: Thomas Alva Edison
1877: Microphone: Emile Berliner
1878: Cathode ray tube: William Crookes
1878: Light bulb patent, Joseph Wilson Swan (British)
1878: Rebreather: Henry Fleuss
1879: Light bulb patent, Woodward and Evans (Canada)
1879: Pelton turbine: Lester Pelton
1879: Cash register: James Ritty
1880: Light bulb patent, Thomas Edison (US)
1880: Photophone: Alexander Graham Bell
1880: Roll film: George Eastman
1880: Safety razor: Kampfe Brothers
1880: Seismograph: John Milne
1881: Metal detector: Alexander Graham Bell
1882: Electric fan: Schuyler Skaats Wheeler
1882: Blowtorch: Carl Rickard Nyberg
1883
U.S. and Canadian railroads adopt four standard time zones, Sanford
Fleming
1883: Two-phase (alternating current) induction motor: Nikola Tesla
1884: Linotype machine: Ottmar Mergenthaler
1884: Recording data on a machine readable medium, the Punched card:
Herman Hollerith
1884: Trolley car, (electric): Frank Sprague, Charles Van Depoele
1885: Automobile patent granted (internal combustion engine
powered): Karl Benz, first automobile put into production
1885: Machine gun: Hiram Stevens Maxim
1885: Motorcycle: Gottlieb Daimler and Wilhelm Maybach
1885: Alternating current transformer: William Stanley
1885: Safety bicycle: John Kemp Starley
1886: Dishwasher: Josephine Cochrane
1886: Gasoline engine: Gottlieb Daimler
1886: Improved phonograph cylinder: Tainter & Bell
1887: Monotype machine: Tolbert Lanston
1887: Contact lens: Adolf E. Fick, Eugčne Kalt and August Muller
1887: Gramophone record: Emile Berliner
1887: Ceiling fan: Philip Diehl
1888: Polyphase AC Electric power system: Nikola Tesla (30 related
patents.)
1888: Kodak hand camera: George Eastman
1888: Ballpoint pen: John Loud
1888: Harvester-thresher: Matteson (?)
1888: Kinematograph: Augustin Le Prince
1889: Northrop Loom: Draper Corporation, James Henry Northrop
1891: Escalator: Jesse W. Reno
1891: Thermal cracking process: Vladimir Shukhov
1891: Zipper: Whitcomb L. Judson
1891: Carborundum: Edward G. Acheson
1891: Modern adjustable spanner: Johan Petter Johansson
1892
Charles and Frank Duryea perfect first automobile.
1892: Color photography: Frederic E. Ives
1892: Automatic telephone exchange (electromechanical): Almon
Strowger - First in commercial service.
1893: Carburetor: Donát Bánki and János Csonka
1893: Tuned Wireless communication (Radio), Nikola Tesla.
1894: Radio transmission: Jagdish Chandra Bose in Bengal
1894: Milking machine: Gustaf de Laval
1895: Diesel engine: Rudolf Diesel
1895: Radiotelegraph: Guglielmo Marconi
1896: Vitascope: Thomas Armat
1897:
First electrified U.S. subway opens in Boston.1897: Modern escalator: Jesse W. Reno
1898: Tapered roller bearing: Henry Timken
1898: Remote control: Nikola Tesla
1899: Iron-mercury coherer with telephone detector: Jagdish Chandra
Bose in Bengal
1899: Automobile self starter: Clyde J. Coleman
1899: Magnetic tape recorder: Valdemar Poulsen
1899: Gas turbine: Charles Curtis
 20th century
20th century
1900: Rigid dirigible airship: Ferdinand Graf von Zeppelin
1900: Self-heating can
1900s: Microwave optics: Jagdish Chandra Bose in Bengal
1900s: Crescograph: Jagdish Chandra Bose in Bengal
1901: Mercury vapor lamp: Peter C. Hewitt
1901: Disposable razor blade: King C. Gillette
1901: Vacuum cleaner: Hubert Booth
1901: Gauge blocks: Carl Edvard Johansson
1902: Ostwald process: Wilhelm Ostwald
1902: Air Conditioner: Willis Carrier
1902: Neon lamp: Georges Claude
1902: Radio telephone: Valdemar Poulsen, Reginald Fessenden
1902: Rayon cellulose ester: Arthur D. Little
1903: Electrocardiograph (EKG): Willem Einthoven
1903: Powered, controlled airplane: Wilbur Wright and Orville Wright
1904: Thermionic valve: John Ambrose Fleming
1904: Tractor: Benjamin Holt
1905: Radio tube diode: John Ambrose Fleming
1906: Sonar (first device): Lewis Nixon
1907: Helicopter: Paul Cornu
1907: Radio tube triode: Lee DeForest
1907: Washing machine, (electric): Alva Fisher (Hurley Corporation)
1908: Cellophane: Jacques E. Brandenberger
1908: Geiger counter: Hans Geiger and Ernest Rutherford
1908: Gyrocompass: Hermann Anschütz-Kaempfe
1908: Haber process: Fritz Haber
1909: Bakelite: Leo Baekeland
1909: Gun suppressor: Hiram Percy Maxim
1910: Braces on teeth: Joseph Clide
1910: Neon lighting: Georges Claude
1910: Thermojet engine: Henri Coandă
1911: Gyrocompass: Elmer A. Sperry
1911: Automobile self starter (perfected): Charles F. Kettering
1911: Hydroplane: Glenn Curtiss
1913: Bra: Mary Phelps Jacob
1913: Crossword: Arthur Wynne
1913: Parachute: Štefan Banič
1913: Radio receiver: Ernst Alexanderson, Reginald Fessenden
1913: Stainless steel: Harry Brearley
1913: X-Ray (coolidge tube): William D. Coolidge[228]
1914: Radio transmitter triode mod.: Ernst Alexanderson
1914: Liquid fuel rocket: Robert Goddard
1914: Tank, military: Sir William Ashbee Tritton and Major Walter
Gordon Wilson[229]
1915: Tungsten Filament: Irving Langmuir
1915: Pyrex: Corning Inc.
1916: Browning Gun: John Browning
1916: Thompson submachine gun: John T. Thompson
1917: Sonar echolocation: Paul Langevin
1917: Cruise missile: Charles Kettering
1918: Interrupter gear: Anton Fokker
1918: Radio crystal oscillator: A.M. Nicolson
1919: Flip-flop circuit: William Eccles and F. W. Jordan
1919: Theremin: Leon Theremin
1920: Saha ionization equation: Meghnad Saha[230]
1921: Polygraph: John A. Larson
1922: Radar: Robert Watson-Watt, A. H. Taylor, L. C. Young, Gregory
Breit, Merle Antony Tuve
1922: The absorption refrigerator: Baltzar von Platen
1923: Sound film: Lee DeForest
1923: Television Electronic: Philo Farnsworth
1923: Wind tunnel: Michael Max Munk
1923: Autogyro: Juan de la Cierva
1923:
First diesel locomotive demonstrated.
1923: Xenon flash lamp: Harold Edgerton
1925: Ultra-centrifuge: Theodor Svedberg - used to determine
molecular weights
1925: Field effect transistor patent: Julius Edgar Lilienfeld
1925: Television Nipkow System: C. Francis Jenkins
1926: Television Mechanical Scanner: John Logie Baird
1926: Aerosol spray: Rotheim
1927: Mechanical cotton picker: John Rust
1928: Sliced bread: Otto Frederick Rohwedder
1928: Electric dry shaver: Jacob Schick
1928: Antibiotics: Alexander Fleming (initial discovery of
penicillin)
1928: Preselector gearbox: Walter Gordon Wilson
1928: Raman effect: Sir Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman
1929: Electroencephelograph (EEG): Hans Berger
1929: Kinescope (CRT):Vladimir Zworykin
1920s: Band aid: Earle Dickson
1920s: Man-made Insulin: Paul Langerhans
1920s: Mechanical potato peeler: Herman Lay
1930: Neoprene: Wallace Carothers
1931: Radio telescope: Karl Jansky Grote Reber
1931: Iconoscope: Vladimir Zworykin
1934: Hammond Organ: Laurens Hammond
1935: Microwave RADAR: Robert Watson-Watt
1935: Nylon: Wallace Carothers
1935: Spectrophotometer: Arthur C. Hardy
1935: Casein fiber: Earl Whittier Stephen
1937: Turboprop engine: György Jendrassik
1937: Jet engine: Frank Whittle and Hans von Ohain
1937: O-ring: Niels Christensen
1937: Nylon: Wallace H. Carothers
1938: Ballpoint pen: Laszlo Biro
1938: xerography: Chester Carlson
1938: Fiberglass: Russell Games Slayter John H. Thomas
1938: LSD: Albert Hofmann
1939: Helicopter: Igor Sikorsky
1939: View-master: William Gruber
1939: Automated teller machine: Luther George Simjian
1941: Computer: Konrad Zuse
1941: Velcro: George de Mestral
1942: Bazooka Rocket Gun: Leslie A. Skinner C. N. Hickman
1942: Nuclear reactor: Enrico Fermi
1942: Undersea oil pipeline: Hartley, Anglo-Iranian, Siemens in
Operation Pluto
1943: Aqua-Lung: Jacques-Yves Cousteau and Emile Gagnan
1944: Electron spectrometer: Deutsch Elliot Evans
1944: Fire balloon in Japan
1945: Slinky: Richard James and Betty James
1945: Microwave oven: Percy L. Spencer
1945: Nuclear weapons (note: chain reaction theory was made in
1933):Manhattan Project
1946: Microwave oven: Percy Spencer
1946: Mobile Telephone Service (Radio): AT&T and Southwestern Bell
1946: Bikini: Louis Réard
1947: Transistor: William Shockley, Walter Brattain, John Bardeen
1947: Polaroid camera: Edwin Land
1948: Long Playing Record: Peter Carl Goldmark
1948: Holography: Dennis Gabor
1949: Atomic clocks
1949: Radiocarbon dating: Willard Libby
1950: Credit card: Frank X. McNamara
1951: Combined oral contraceptive pill: Djerassi, Miramontes, and
Rosenkranz
1951: Liquid Paper: Bette Nesmith Graham
1951: Nuclear power reactor: Walter Zinn
1952: Floppy disk: Yoshiro Nakamatsu
1952: Optical fiber: Narinder Singh Kapany
1952: Fusion bomb: Edward Teller and Stanislaw Ulam
1952: Hovercraft: Christopher Cockerell
1953: MASER: Charles Townes
1953: Medical ultrasonography
1954: Radar gun: Bryce K. Brown
1954: Synthetic diamond: Tracy Hall
1954: Geodesic dome: Buckminster Fuller
1955: Hard Drive: Reynold Johnson with IBM
1955: Video phone: Gregorio Y. Zara in the Philippines
1956: Digital clock
1956: Videocassette recorder: Ampex
1957: Jet Boat: William Hamilton
1958: Integrated circuit: Jack Kilby of Texas Instruments, Robert
Noyce at Fairchild Semiconductor
1958: Communications satellite: Kenneth Masterman-Smith
1958: Implantable pacemaker: Rune Elmqvist
1960: Laser: Theodore Harold Maiman
1961: Optical disc: David Paul Gregg
1961: Cochlear implant: William House
1961: Human spaceflight: Yuri Gagarin, Sergey Korolyov, Kerim
Kerimov
1962: Light-emitting diode (LED): Nick Holonyak
1962: Space observatory: Ball Brothers Aerospace Corporation
1963: Computer mouse: Douglas Engelbart
1967: Space dock: Kerim Kerimov
1967: Automatic Teller Machine: John Shepherd-Barron
1967: Hypertext: Andries van Dam and Ted Nelson
1968: Video game console: Ralph H. Baer
1960s: Packet switching: Paul Baran and Donald Davies, independently
1969: ARPANET (first wide-area packet switching network): United
States Department of Defense
1969: Digital Photography, charge coupled device Willard Boyle and
George E. Smith
1970: Relational database management system: Edgar F. Codd
1971: Space station: Kerim Kerimov
1971: E-mail: Ray Tomlinson
1971: Liquid Crystal Display: James Fergason
1971: Microprocessor: Federico Faggin and Ted Hoff
1971: Pocket calculator: Sharp Corporation
1971: Magnetic resonance imaging: Raymond V. Damadian
1972: Computed tomography: Godfrey Newbold Hounsfield
1973: Hybrid rice in China
1973: Ethernet: Bob Metcalfe and David Boggs
1973: Genetically modified organism: Stanley Norman Cohen and
Herbert Boyer
1973: Personal computer: Xerox PARC
1974: Microfinance: Muhammad Yunus
1974: Rubik's Cube: Ernő Rubik
1974: Hybrid vehicle: Victor Wouk
1975: DNA sequencing by chain termination Frederick Sanger
1975: Digital camera: Steven Sasson
1976: Gore-Tex fabric: W. L. Gore
1977: Personal stereo: Andreas Pavel
1977: Mobile phone (cellphone): Bell Labs
1978: Spreadsheet: Dan Bricklin
1980: Compact Disc: Philips Electronics, Sony Corp
1981: Scanning tunneling microscope: Gerd Karl Binnig and Heinrich
Rohrer
1982: Insulated gate bipolar transistor: Hans Becke and Carl
Wheatley RCA
1982: ACE inhibitor: John R. Vane
1982: Artificial heart: Robert Jarvik, incorporating modifications
to earlier experimental designs
1983: Camcorder: Sony
1983: Internet: first TCP/IP network: Robert E. Kahn, Vint Cerf and
others
1984: Lithotripsy: Claude Dornier
1985: Polymerase chain reaction: Kary Mullis
1985: DNA fingerprinting: Alec Jeffreys
1987: Statin, cholesterol drug: Carl Hoffman
1987: Digital Light Processing: Dr. Larry Hornbeck, Texas
Instruments
1990: World Wide Web: Tim Berners-Lee
1993: Global Positioning System: United States Department of Defense
1993: Blue LED: Shuji Nakamura
1994: Wiki: Ward Cunningham
1997: Non-mechanical digital audio player: SaeHan Information
Systems
 3rd
millennium 3rd
millennium
21st century
2001: Self-contained artificial heart
2001: PageRank: Sergey Brin Larry Page
2001: Human genome sequenced.
|

